Muscles of the Medial Compartment of the Thigh
This is an excerpt from The Pocket Atlas of Skeletal Muscles by Chris Jarmey.

Gracilis
Latin, gracilis, slender, delicate.
Origin
A line on the external surfaces of the pubis, the inferior pubic ramus, and ramus of the ischium.
Insertion
Medial surface of proximal shaft of tibia.
Nerve supply
Obturator nerve L2, 3.
Blood supply
Obturator artery
via internal iliac artery (a branch of common iliac artery from abdominal aorta).
Can also be supplied by medial circumflex femoral artery (from deep femoral artery).
Action
Adducts thigh at hip joint. Flexes leg at knee joint.
Pectineus
Latin, pecten, comb; pectinatus, comb shaped.
Origin
Pecten pubis and adjacent bone of pelvis.
Insertion
Oblique line, from base of lesser trochanter to linea aspera of femur.
Nerve supply
Femoral nerve L2, 3.
Blood supply
Medial circumflex femoral artery
(from deep femoral artery).
Action
Adducts and flexes thigh at hip joint.
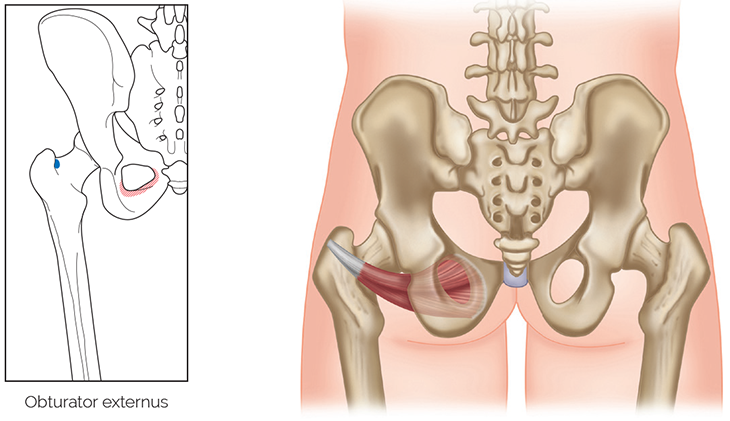
Obturator Externus
Latin, obturare, to obstruct; externus, external.
Origin
External surface of obturator membrane and adjacent bone.
Insertion
Trochanteric fossa.
Nerve supply
Posterior division of obturator nerve L3, 4.
Blood supply
Obturator artery
via internal iliac artery (a branch of common iliac artery from abdominal aorta), plus can also be supplied by medial circumflex arteries (from deep femoral artery).
Action
Laterally rotates thigh at hip joint.
SHOP

Get the latest insights with regular newsletters, plus periodic product information and special insider offers.
JOIN NOW
Latest Posts
- How do I integrate nutrition education into PE?
- How does the support of friends and family influence physical activity?
- What makes the Physical Best approach unique?
- Strength training gimmicks . . . or not?
- How do vitamins and minerals support our bodies?
- Why do many people have difficulty losing weight?


